These are what i get from the 2nd meeting in algorithm & programming
Operator, Operand, and Arithmetic:
–Operator and Operand Introduction
–Assignment Operators
–Arithmetic Operators
–Relational Operators
–Conditional Expressions
–Logical Operators
–Bitwise Operators
–Pointer Operators
–Precedence and Associative
Operator and Operand Introduction
- Operator is a symbol to process values in result for a new value
- Operand is part which specifies what data is to be manipulated or operated on
- Example :
C = A + B
(= and + sign are operators, A, B and C are operands)
- Based on its operand number, operator can be divided into three:
–Unary operator (needs one operand)
–Binary operator (needs two operands)
–Ternary operator (needs three operands)
Assignment Operators
- Example:
x = 2; // constant
x = y; // other variable
x = 2 * y; // expression
x = sin (y); // function
- Type of the result will follow the left hand side operand
int x = 7/2; /*x value is 3 not 3.5*/
float y = 3; /*y value is 3.000 */
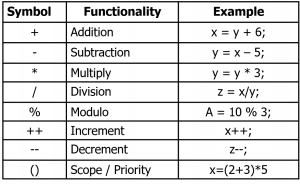
Arithmetic Operators
- Modulo
–Symbol : %
–Binary operator
–To find reminder of a division
–N % 2, can be used to find an odd or even number
- N % 2 = 0 ® N is even
- N % 2 = 1 ® N is odd
- Increment and Decrement
–Symbol : ++(increment), –(decrement)
–Unary operator
–Increase (++) and decrease (–) the value of a variable by 1.
–Its position can be in the front (pre) or after (post) a variable.
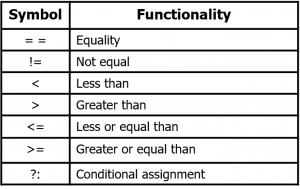
Relational Operators
Use to compare to values with TRUE or FALSE result
FALSE in C language equals to the value of zero
TRUE on the other hand not equal to zero
TRUE set by a C program at run time equal to the value of one
Conditional Expressions
- Given the following statement:
if(a > b) z = a;
else z = b;
- The above statement can be reformed to a conditional expression
- Conditional expression using ternary operator : ‘?’ and ‘:’
- Syntax :
exp1 ? exp2 : exp3;
- Example (similar meaning with the above statement):
z = (a > b) ? a : b;